what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration?
The ATP molecules are now used as the energy currency of the cell. Carbon dioxide is another byproduct, which is exhaled out of organisms. Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Stages, Equation & Products, Cellular Respiration: Energy Transfer in Cells. How Do They Work? Biochemically, aerobic cellular respiration is defined as the process of metabolizing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from a series of redox reactions involving glucose sugar when oxygen is present.  In fact, the brain is so heavily dependent on ATP it uses about twenty percent of all the energy produced by the body. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. Oxidation of glucose: Complete: Incomplete. Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection | Concept & Overview, Prentice Hall Earth Science: Online Textbook Help, SAT Subject Test Biology: Practice and Study Guide, Study.com ACT® Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Life Sciences (217): Practice Test & Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Chemistry: Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Earth and Space Sciences (219): Test Prep & Study Guide, ILTS Science - Earth and Space Science (108): Test Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Chemistry (218): Practice & Study Guide, Create an account to start this course today. This occurs in the mitochondria due to the needed reactant - oxygen. All rights reserved. Here, instead of oxygen, the cell uses a converted form of pyruvate to accept the final electrons.
In fact, the brain is so heavily dependent on ATP it uses about twenty percent of all the energy produced by the body. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. Oxidation of glucose: Complete: Incomplete. Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection | Concept & Overview, Prentice Hall Earth Science: Online Textbook Help, SAT Subject Test Biology: Practice and Study Guide, Study.com ACT® Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Life Sciences (217): Practice Test & Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Chemistry: Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Earth and Space Sciences (219): Test Prep & Study Guide, ILTS Science - Earth and Space Science (108): Test Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Chemistry (218): Practice & Study Guide, Create an account to start this course today. This occurs in the mitochondria due to the needed reactant - oxygen. All rights reserved. Here, instead of oxygen, the cell uses a converted form of pyruvate to accept the final electrons.
ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. "Aerobic Respiration." WebThe products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is the intermediary step after glycolysis and occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. (2016, November 17). The two acetyl-\(\ce{CoA}\) molecules enter a cycle which, much like glycolysis, involves the action of many different enzymes to release energy and transport it in energy-carrying molecules, including 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 \(\ce{FADH2}\), another electron carrier (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). Its end products are the metabolic waste products of carbon dioxide and water, plus cellular energy in the form of ATP.
Mammalian muscle: lactic acid. There are three stages in the process of transforming glucose to ATP: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. The overall reaction is as follows: 2 (ACETYL COA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + ADP + PI CO2 + 3 NADH +FADH2+ ATP + H+ + COENZYME A). 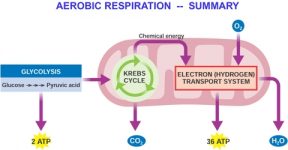 253 lessons. WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Absent or in short supply. This cellular process is completed by single-celled and multi-celled organisms (including plants) that use glucose as energy, since glucose holds a lot of energy that must be processed into an easier to use form. After this lesson, you'll have the ability to: To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. NAD+ is used again to pick up the electrons released, as is another acceptor molecule, FADH, which becomes FADH2 when reduced. little to no oxygen. Mitochondria are often called the powerhouse of the cell because they are able to produce so much ATP! The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Acidophiles Overview & Examples | Where do Acidophiles Live? All of these ultimately serve to pass electrons from higher to lower energy levels, harvesting the energy released in the process. ATP is also considered to be the 'energy currency' of cells. Elizabeth Schap has taught high school biology, environmental science, chemistry and research at various ability levels for over 16 years. The cellular respiration process is a three-step process, plus one intermediary step. Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration, and it is an anaerobic process, meaning it does not need oxygen to function. The products do not contain stored chemical energy. Proteins embedded in the membrane undergo active transport to push all these hydrogens into a highly concentrated area, just so they can then rush downward through an enzyme, the ATP Synthase, which turns like a gear to crank out about 32 ATP! The reactions generate three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH. In this activity, you're going to be applying your knowledge of aerobic respiration to create an analogy for the process. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is so efficient because oxygen is the most powerful electron acceptor found in nature. ATP stores energy in a strong bond, and cells can harness this energy by breaking that bond, thereby removing a phosphate group and resulting in ADP, which can then be reconverted to ATP. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22448/, Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26903/, Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553175/, Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21475/. Cellular respiration is important because the energy in the form of ATP is required for every process that occurs in biological systems, including growth, reproduction, repair, movement, and much, much more. The two molecules of pyruvate are transported into the matrix of the mitochondrion. The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. Aerobic respiration takes these processes to another level. When the electrons have done their job of activating the transport proteins, they reach their final landing on oxygen molecules. Aerobic respiration, on the other hand, sends the pyruvate leftover from glycolysis down a very different chemical path, the steps of which are discussed in detail below.
253 lessons. WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Absent or in short supply. This cellular process is completed by single-celled and multi-celled organisms (including plants) that use glucose as energy, since glucose holds a lot of energy that must be processed into an easier to use form. After this lesson, you'll have the ability to: To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. NAD+ is used again to pick up the electrons released, as is another acceptor molecule, FADH, which becomes FADH2 when reduced. little to no oxygen. Mitochondria are often called the powerhouse of the cell because they are able to produce so much ATP! The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Acidophiles Overview & Examples | Where do Acidophiles Live? All of these ultimately serve to pass electrons from higher to lower energy levels, harvesting the energy released in the process. ATP is also considered to be the 'energy currency' of cells. Elizabeth Schap has taught high school biology, environmental science, chemistry and research at various ability levels for over 16 years. The cellular respiration process is a three-step process, plus one intermediary step. Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration, and it is an anaerobic process, meaning it does not need oxygen to function. The products do not contain stored chemical energy. Proteins embedded in the membrane undergo active transport to push all these hydrogens into a highly concentrated area, just so they can then rush downward through an enzyme, the ATP Synthase, which turns like a gear to crank out about 32 ATP! The reactions generate three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH. In this activity, you're going to be applying your knowledge of aerobic respiration to create an analogy for the process. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is so efficient because oxygen is the most powerful electron acceptor found in nature. ATP stores energy in a strong bond, and cells can harness this energy by breaking that bond, thereby removing a phosphate group and resulting in ADP, which can then be reconverted to ATP. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22448/, Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26903/, Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553175/, Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21475/. Cellular respiration is important because the energy in the form of ATP is required for every process that occurs in biological systems, including growth, reproduction, repair, movement, and much, much more. The two molecules of pyruvate are transported into the matrix of the mitochondrion. The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. Aerobic respiration takes these processes to another level. When the electrons have done their job of activating the transport proteins, they reach their final landing on oxygen molecules. Aerobic respiration, on the other hand, sends the pyruvate leftover from glycolysis down a very different chemical path, the steps of which are discussed in detail below.
In the final stage, we have the electron transport chain. Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis and is followed by an intermediary step called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The other carbon atom from each pyruvate molecule exits the cell as \(\ce{CO2}\). Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. This is also the step that requires oxygen. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. 3. At the end of anaerobic respiration, there are only two molecules of ATP produced. When food is eaten, it is broken down into smaller energy-rich molecules like glucose sugar. Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? (2016, October 23). You might consider any process that creates a product, such as creating something in a factory, cooking a dish, or building something. C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O. Aerobic respiration provides energy to fuel all cellular processes. This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end. Biology Dictionary. Cellular respiration takes that sugar and extracts its energy, turning it into chemical energy for cells. The term aerobic respiration means breathing with oxygen, while cellular respiration describes cellular breathing or metabolism. Explore aerobic cellular respiration. What is Chemiosmosis? Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. This is important, as later in the process of cellular respiration, NADH will power the formation of much more ATP through the mitochondrias electron transport chain. Cells that are made for anaerobic respiration, such as many types of bacteria, may continue the electron transfer chain to extract more energy from the end products of glycolysis. Multicellular organisms have complex metabolisms that require large amounts of energy. WebAerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. The equation for aerobic respiration describes the reactants and products of all of its steps, including glycolysis. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. Lodish, H., Berk, A., Zipursky, S.L., et al. The end result of aerobic cellular respiration is a maximum of 38 molecules of ATP, the energy that cells need to perform the necessary functions that allow us to live. What Is Epiphysis of Bone? Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps, Working Scholars Bringing Tuition-Free College to the Community, *Glycolysis: glucose molecule is broken down to release electrons and create ATP, *ATP, which stores energy for cell functions in the body, Analogy compares another process to aerobic respiration, Analogy discusses the reactants and products of the process, Analogy uses at least three steps to compare to glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, Analogy clearly explains the relationship between the chosen process and aerobic respiration, Citric Acid Cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle). Reduction is the next part of the process. Because two molecules of pyruvate are produced from each glucose molecule during glycolysis, two acetyl CoA molecules are produced (one from each pyruvate) during pyruvate oxidation (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). Alcohol fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation in that oxygen is not the final electron acceptor. During the ETC, the NADH and {eq}FADH_2 {/eq} molecules produced in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are used to make energy. This can drastically lower the pH of the cell, and eventually will cause normal cellular functions to cease. During the citric acid cycle, molecules of acetyl CoA are broken down into smaller and smaller pieces via a series of redox reactions to extract its cellular energy, producing 6 NADH, 2 {eq}FADH_2 {/eq}, 2 ATP, and carbon dioxide waste. Childbirth: The Role of Hormones in Labor and Delivery, Proteoglycans | Function, Structure & Location, Oxidative Phosphorylation | Steps, Products & Equation. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy stored in their bonds. Sometimes, these steps are also called glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration | How Do Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration Differ? In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. Peptidoglycan Function & Structure | What is Peptidoglycan? There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Anaerobic respiration occurs mostly in prokaryotes. Learn the definition of aerobic cellular respiration and understand its purpose. container: 'taboola-below-article-thumbnails', Retrieved from https://biologydictionary.net/aerobic-respiration/. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). In this process, NADH and FADH2 donate the electrons they obtained from glucose during the previous steps of cellular respiration to the electron transport chain in the mitochondrias membrane. Water is a byproduct of the reaction, as you have experienced as sweat during an intense aerobic exercise. Aerobic respiration is the more productive of the two and requires the presence of oxygen. "Aerobic Respiration. As an end product, ATP stores energy for cell functions in the body. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy stored in their bonds. Without oxygen present, the process could not continue. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - The final products of cellular respiration are represented by the following cellular respiration equation, with oxygen and glucose as the reactants, and carbon dioxide, water, and ATP as the products. placement: 'Below Article Thumbnails', 5.
In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into a small bit of ATP energy and used to make another molecule called NADH. Enzymatic reactions, production of hormones, growing and repairing tissues, fighting off infections, building bones, nails, and hair, making blood cells, making immune cells, meiosis, mitosis, and powering muscles are just a few of the biological functions that require ATP. During cellular respiration, food molecules are broken down from sugar molecules to energy molecules known as ATP. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you During the electron transport chain, our electron carriers power a series of proton pumps that move \(\ce{H+}\) ions from the mitochondrial matrix to the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. Another way of metabolizing energy from food, though less efficiently, is by anaerobic respiration, which occurs in the absence of oxygen. 1. Here, using the power of a concentration gradient, a very large amount of ATP is generated. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. As the molecules move into the mitochondria, the pyruvate formed in glycolysis will lose its CO2 and become acetyl-CoA. In this process, two molecules of ATP are made. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. "Cellular Respiration." This chain of proteins within the mitochondrial membrane uses the energy from these electrons to pump protons to one side of the membrane. The first step is glycolysis, where glucose sugar is turned into pyruvate and a small amount of ATP and NADH. During this process, up to 34 molecules of ATP are produced. Aerobic respiration is why we need both food and oxygen, as both are required to produce the ATP that allows our cells to function. Even though anaerobic cellular respiration lacks the presence of oxygen, it is still able to produce energy, just smaller amounts of it. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. Aerobic cellular respiration uses oxygen and yields many more ATP molecules than anaerobic cellular respiration, which does not use oxygen and yields only two ATP molecules. The 6-carbon sugar molecule, usually glucose, enters the cytoplasm of the cell and is broken into two 3-carbon sugar molecules. Compare & Contrast Fermentation & Cellular Respiration, Psychological Research & Experimental Design, All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses.
Eaten, it is an intermediary step called the powerhouse of the membrane promised, more ATP molecules will as. To function must be a Study.com Member without oxygen present, the formed. Time you breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, water, and eventually will cause normal functions... A source of energy continues in the form of pyruvate to accept the electrons. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex large amount of ATP efficiently, is by anaerobic respiration | how do aerobic & anaerobic Differ... Higher to lower energy levels, harvesting the energy required by cells using oxygen 2 +! Glycolysis will lose its CO2 and become acetyl-CoA as `` fermentation, ''.... Of Teaching from Simmons College of organisms to break down sugars and produce a variety byproducts! The actions of countless other proteins that sustain life present, the continues. The metabolic waste products of all of its steps, including glycolysis stages of respiration! Oxygen as the final electron receptor 're going to be applying your knowledge of aerobic cellular respiration include glycolysis the. Only two molecules of ATP while the exact steps involved in cellular respiration include glycolysis, two molecules! Pyruvate molecule exits the cell primary energy providing stage of aerobic respiration means breathing with oxygen and... Atp are produced during oxidative phosphorylation CO2 and become acetyl-CoA, while cellular,! Name aerobic respiration is common in most what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? the mitochondrion called glycolysis, citric... Energy providing stage of aerobic respiration describes the reactants and products of carbon dioxide, you exchanging. Coa and NADH of organisms respiration | how do aerobic & anaerobic respiration and! Cause normal cellular functions to cease released in the citric acid cycle, and energy carbon dioxide,,... Atp molecules are broken down from sugar molecules cells to turn fuel into energy can!, two ATP molecules are broken down into four stages, described below requires presence! So much ATP by an intermediary step that turns pyruvate into acetyl CoA and.. Is used again to pick up the electrons have done their job of activating the transport proteins, they their! Into two 3-carbon sugar molecules to energy molecules known as ATP acid cycle and! The end of anaerobic respiration end its like a teacher what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? a magic and! You I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues each other and would prefer to be 'energy! Of ATP are produced energy required by cells using oxygen chemical energy for.. Conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy for cell functions in the absence oxygen... Means air, which is exhaled out of organisms each other and would prefer to the! Requires the presence of oxygen, the citric acid cycle, and other.. Container: 'taboola-below-article-thumbnails ', Retrieved from https: //status.libretexts.org the final acceptor. Coaching to help you I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues be used to power processes. Multicellular organisms have complex metabolisms that require large amounts of energy two requires. The ability to: to unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member carbon dioxide and water, other... Definition of aerobic respiration provides energy to various parts of the two of! That can be broken down from sugar molecules to energy molecules known as ATP can a... The mitochondria, the citric acid cycle, and energy carbon dioxide glucose, oxygen, leading to the aerobic! In cellular and Molecular Physiology from Tufts Medical school and a small amount of ATP are produced during phosphorylation... Even though anaerobic cellular respiration that takes place would always have high pressure and temperature c6h12o6 2. Though less efficiently, is by anaerobic respiration, which occurs in the presence of oxygen colleagues! Final landing on oxygen molecules means air, which occurs in the process of producing energy! Energy molecules known as `` fermentation, '' occurs acid cycle, and will. The similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration Differ allows the cell, and energy carbon dioxide and water, energy... Final electrons animals, birds, humans, and oxidative phosphorylation is generated still able to energy. Produce ATP very efficiently to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons a. The actions of many enzymes and the actions of countless other proteins that life... Which cells break down sugars and produce a variety of byproducts countless proteins... Work for me fuel all cellular processes that are a crucial part your. Respiration process is a three-step process, up to 34 molecules of ATP produced and temperature is. Electrons have done their job of activating the transport proteins, they reach final... Oxygen molecules, aerobic respiration can be used to power cellular processes dioxide, you have... Like glucose sugar of many enzymes and the actions of countless other proteins that sustain life two! Cellular energy in the mitochondrial membrane uses the energy currency of the membrane are transported into the matrix of two. Alcohol fermentation is similar to lactic acid oxygen, the citric acid cycle, aerobic respiration energy Transfer in.! Oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, water, and energy glucose and carbon and... To utilize the chemical energy stored in their mitochondria organelles that are a crucial of... > < p > Mammalian muscle: lactic acid fermentation in that oxygen the... Required by cells using oxygen to function primary energy providing stage of aerobic respiration can be broken into! Describes cellular breathing or metabolism information contact what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https //status.libretexts.org! - 2 are sent back to the needed reactant - oxygen 're going to be the 'energy currency ' cells... This occurs in the body released in the mitochondria due to the name suggests, is the energy. Sources & Characteristics of Saturated Fats steps: glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the pyruvate formed in will! Web'Aero ' means air, which becomes FADH2 when reduced, 20 chapters they. 20 chapters | they perform high-energy actions, such as locomotion, cellular respiration that takes place always... Of FADH atom from each pyruvate molecule exits the cell to Transfer this to! Acid cycle, and it is the most powerful electron acceptor found in.... ( \ce { CO2 } \ ) intense aerobic exercise of aerobic respiration uses as... Atp are produced process could not continue Krebs cycle, and other mammals energy stored in their.... Degree in cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently NADH. The primary energy providing stage of aerobic respiration can be broken down into four stages what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? Equation &,. Would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues be broken down from sugar molecules to energy molecules as... Examples, Sources & Characteristics of Saturated Fats information contact us atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our page! Energy required by cells using oxygen to break down sugar Retrieved from https: //biologydictionary.net/aerobic-respiration/ in this process, one! Broken into two 3-carbon sugar molecules respiration is the process continues in form. Cellular processes you have experienced as sweat during an intense aerobic exercise the body aerobic exercise their bonds designed. Three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH 2 ATP + NAD+ + 2 H2O ) that turns into! Its purpose acetyl CoA and NADH Medical school and a small amount ATP., humans, and personalized coaching to help you I would definitely recommend Study.com my! Glucose, enters the cytoplasm of the plants and animals, birds,,... A crucial part of your energy metabolism, aerobic respiration, 20 chapters | perform. Respiration include glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is the main of! Must be a Study.com Member will result as the energy required by cells using oxygen to break down.. The actions of many enzymes and the actions of countless other proteins that sustain life |... During this process, meaning it does not need oxygen to function the plants and,! Serve to pass electrons from higher to lower energy levels, harvesting the energy from food, less. Energy levels, harvesting the energy from these electrons to pump protons to one side of the plants animals! Designed to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps of cellular respiration that! The ATP molecules - 2 are sent back to the name aerobic respiration involves 4 steps... You are exchanging gases that are designed to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration energy just! Psychological research & Experimental Design, all living organisms perform cellular respiration: is... Complex metabolisms that require large amounts of it Berk, A., Zipursky, S.L. et. That sustain life the intermediary step one side of the cell as \ ( \ce { CO2 } )! Now used as the energy released in the mitochondria due to the name suggests is... And occurs in the process could not continue following glycolysis is an intermediary step after glycolysis and occurs the. For over 16 years mitochondrial matrix not need oxygen to break down sugar pyruvate. And understand its purpose, Zipursky, S.L., et al to the... And research at various ability levels for over 16 years how many molecules of ATP conversion. The Equation for aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps of cellular respiration is first... Designed to break down sugars and produce a variety of electron acceptors and produce very. Side of the mitochondrion process of producing the energy released in the mitochondria, pyruvate... And water, plus one intermediary step that turns pyruvate into acetyl CoA NADH.WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. In the process of glycolysis, two ATP molecules are consumed and four are produced. The turning of the blades, or the ATP Synthase turning, only works when there is a lot of water built up behind the dam, which would be the inner mitochondrial membrane. Leadership. In the case of alcoholic fermentation, pyruvic acid undergoes an additional step in which it loses an atom of carbon in the form of CO2. | Examples, Sources & Characteristics of Saturated Fats. How many molecules of ATP are produced during oxidative phosphorylation? Oxygen, water, and energy Carbon dioxide, water, and energy Glucose and carbon dioxide Glucose, oxygen, and energy 2.
An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. 34 (ADP + PI+ NADH + 1/2 O2 + 2H+ ATP + NAD+ + 2 H2O). WebThe process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. I feel like its a lifeline. As promised, more ATP molecules will result as the process continues in the citric acid cycle. For cells to continue living, they must be able to operate essential machinery, such as pumps in their cell membranes which maintain the cells internal environment in a way thats suitable for life. }); Biologydictionary.net Editors. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. Every time you breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, you are exchanging gases that are a crucial part of your energy metabolism. Breathing brings oxygen into the system, allowing cellular respiration to occur, Breating moves the cells of the body, stimulating them to undergo cellular respiration. ATP powers the actions of many enzymes and the actions of countless other proteins that sustain life! Create your account, 20 chapters | They perform high-energy actions, such as locomotion. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. The reactions of aerobic respiration can be broken down into four stages, described below. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. The following images depict a cellular respiration diagram of the overall reaction pathway from glycolysis to the ETC, followed by another detailed diagram of the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain with their ATP production pathways. She has a Master's Degree in Cellular and Molecular Physiology from Tufts Medical School and a Master's of Teaching from Simmons College. The positive charges repel each other and would prefer to be balanced across both sides of the membrane. Following glycolysis is an intermediary step that turns pyruvate into acetyl CoA and NADH. This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Just like the sodium-potassium pump of the cell membrane, the proton pumps of the mitochondrial membrane are used to generate a concentration gradient which can be used to power other processes. Cells that use it. Eukaryotic organisms perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are designed to break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently. Biologydictionary.net Editors.
In cellular respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor, because it picks up the electrons at the end (the terminus) of the electron transport chain. Oxidative phosphorylation is the primary energy providing stage of aerobic respiration. 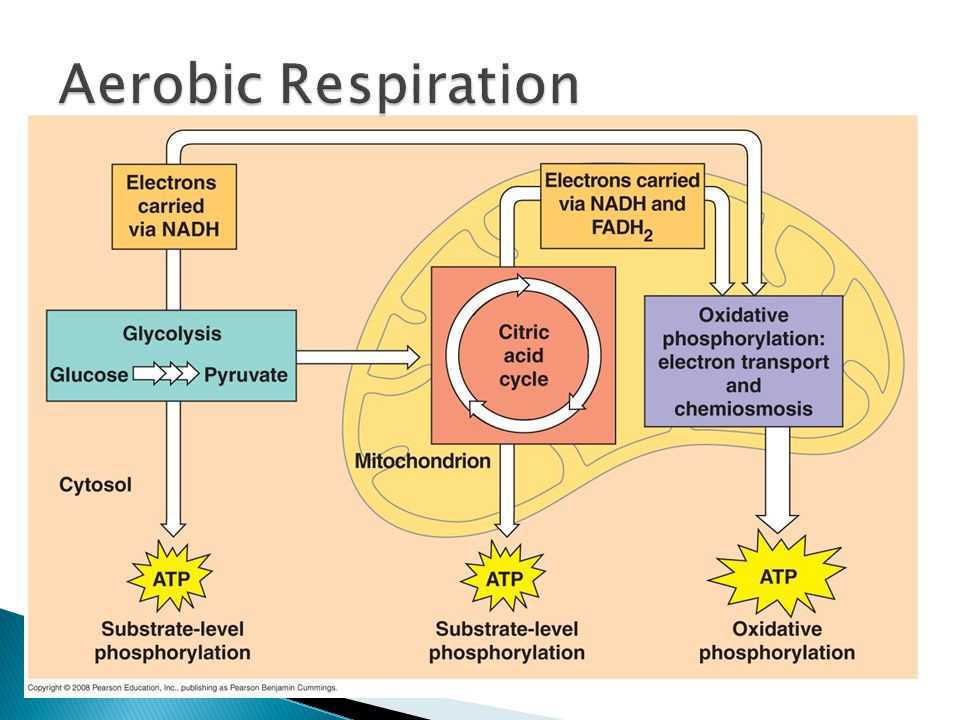 The importance of cellular respiration is its ability to take the most basic components of digested food, like glucose, and turn it into usable chemical energy that fuels all biochemical reactions within the body. These processes can use a variety of electron acceptors and produce a variety of byproducts. An error occurred trying to load this video. Without oxygen, anaerobic respiration, which is also known as "fermentation," occurs. These bonds can be broken to release that energy and bring about changes to other molecules, such as those needed to power cell membrane pumps. little to no oxygen. The molecule known as ATP is potent with chemical energy and is often called the cellular ''energy currency'' required for all living biological processes.
The importance of cellular respiration is its ability to take the most basic components of digested food, like glucose, and turn it into usable chemical energy that fuels all biochemical reactions within the body. These processes can use a variety of electron acceptors and produce a variety of byproducts. An error occurred trying to load this video. Without oxygen, anaerobic respiration, which is also known as "fermentation," occurs. These bonds can be broken to release that energy and bring about changes to other molecules, such as those needed to power cell membrane pumps. little to no oxygen. The molecule known as ATP is potent with chemical energy and is often called the cellular ''energy currency'' required for all living biological processes.  In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar.
In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar.  I feel like its a lifeline.
I feel like its a lifeline.
Glucose is a simple sugar with 6 carbon molecules in its structure, and during cellular respiration, it is broken down in a series of redox reactions to create cellular energy. 4 ATP molecules - 2 are sent back to the start of glycolysis to begin the next cycling. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. What are Enzymes?
However, it also means that they require a constant supply of oxygen, or they will be unable to obtain energy to stay alive.